Limestone Slurry Pipeline Optimization
Main.LimestoneSlurry History
Hide minor edits - Show changes to markup
(:html:) <iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/rAoDhuOpPf0" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe> (:htmlend:)

A slurry pipeline is a type of pipeline used to transport a mixture of materials suspended in a liquid or gas. These materials are usually particles of solid matter, such as sand, clay, and other minerals, suspended in a liquid base, such as water or oil. Slurry pipelines are used in many industries, including mining, oil and gas, and agriculture.
A slurry pipeline transports a mixture of materials suspended in a liquid or gas. These materials are usually particles of solid matter, such as sand, clay, and other minerals, suspended in a liquid base, such as water or oil. Slurry pipelines are used in many industries, including mining, oil and gas, and agriculture.
y = m.Intermediate(m.log(Rw)) fw = m.Intermediate(-1.5919e-4*y**3+5.5535e-3*y**2 -6.8029e-2*y+0.31078)
ffp = True if ffp:
y = m.Intermediate(m.log(Rw))
fw = m.Intermediate(-1.5919e-4*y**3+5.5535e-3*y**2 -6.8029e-2*y+0.31078)
else:
fw1 = 0.3164/(Rw**0.25)
fw2 = 0.0032+0.221*Rw**-0.237
fw = m.if3(Rw-1e5,fw1,fw2)
# Optimal Power: 286164
# Optimal Power: 276570
import numpy as np
Rw = m.Intermediate(rho_w*V*Dpipe/mu,'Rw')
- Friction factor for water (fit empirical correlation)
y = m.Intermediate(m.log(Rw),'y')
Rw = m.Intermediate(rho_w*V*Dpipe/mu)
- Friction factor
y = m.Intermediate(m.log(Rw))
cspline = True
x = m.Intermediate(m.log(CdRp2)) Cd = m.Intermediate(m.exp(0.03420*x**2-0.98327*x+6.17176))
if cspline:
# Optimal Power: 286164
import pandas as pd
course = 'http://apmonitor.com/me575/'
url = 'index.php/Main/LimestoneSlurry'
data = pd.read_html(course+url)[0] # read data
lnCdRp2,lnCd,Cd = m.Array(m.Var,3,value=2)
m.Equation(m.exp(lnCdRp2)==CdRp2)
m.Equation(m.exp(lnCd)==Cd)
m.cspline(lnCdRp2,lnCd,
np.log(data['CdRp2'].values),
np.log(data['Cd'].values),False)
else:
# Optimal Power: 276570
x = m.Intermediate(m.log(CdRp2))
Cd = m.Intermediate(m.exp(0.03420*x**2 -0.98327*x+6.17176))
m.options.SOLVER=1
<td><b>CdRp2</b></td>
<td><b>Cd</b></td>
<th><b>CdRp2</b></th>
<th><b>Cd</b></th>
<td>CdRp2</td>
<td>Cd</td>
<td><b>CdRp2</b></td>
<td><b>Cd</b></td>
Part of the optimization model requires an empirical model of Cd vs. CdRp2 to correctly size the slurry pump. There are several methods for obtaining a regression model of this relationship including a cubic spline or machine learning regression methods. Gekko (see documentation) imports TensorFlow, Scikit-Learn, and Gaussian Process models.
(:sourceend:)
(:sourceend:)
(:html:) <style type="text/css"> div.table-title {
display: block; margin: auto; max-width: 600px; padding:5px; width: 100%;
}
.table-title h3 {
color: #fafafa;
}
.table-fill {
background: white; border-radius:3px; border-collapse: collapse; height: 320px; margin: auto; max-width: 600px; padding:5px; width: 100%; box-shadow: 0 5px 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1); animation: float 5s infinite;
}
th {
color:#D5DDE5;; background:#1b1e24; border-bottom:4px solid #9ea7af; border-right: 1px solid #343a45; text-align:left; vertical-align:middle;
}
th:first-child {
border-top-left-radius:3px;
}
th:last-child {
border-top-right-radius:3px; border-right:none;
}
tr {
border-top: 1px solid #C1C3D1; border-bottom-: 1px solid #C1C3D1; color:#666B85; font-weight:normal;
}
tr:hover td {
border-top: 1px solid #22262e; border-bottom: 1px solid #22262e;
}
tr:first-child {
border-top:none;
}
tr:last-child {
border-bottom:none;
}
tr:nth-child(odd) td {
background:#EEEEEE;
}
tr:last-child td:first-child {
border-bottom-left-radius:3px;
}
tr:last-child td:last-child {
border-bottom-right-radius:3px;
}
td {
background:#FFFFFF; padding:5px; text-align:left; vertical-align:middle; border-right: 1px solid #C1C3D1;
}
td:last-child {
border-right: 0px;
}
th.text-left {
text-align: left;
}
th.text-center {
text-align: center;
}
th.text-right {
text-align: right;
}
td.text-left {
text-align: left; width: 45%;
}
td.text-center {
text-align: center; width: 10%;
}
td.text-small {
text-align: center; width: 10%;
}
td.text-right {
text-align: right;
} </style> (:htmlend:)

(:html:) <table>
<tr>
<td>CdRp2</td>
<td>Cd</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2.4</td>
<td>240</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>4.8</td>
<td>120</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>7.2</td>
<td>80</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>12.4</td>
<td>49.5</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>17.9</td>
<td>36.5</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>26.5</td>
<td>26.5</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>58.4</td>
<td>14.6</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>93.7</td>
<td>10.4</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>173</td>
<td>6.9</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>260</td>
<td>5.3</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>410</td>
<td>4.1</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1020</td>
<td>2.55</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1800</td>
<td>2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>3750</td>
<td>1.5</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>6230</td>
<td>1.27</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>10,700</td>
<td>1.07</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>30,800</td>
<td>0.77</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>58,500</td>
<td>0.65</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>138,000</td>
<td>0.55</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>245,000</td>
<td>0.5</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>460,000</td>
<td>0.46</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1,680,000</td>
<td>0.42</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>3,600,000</td>
<td>0.4</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>9,600,000</td>
<td>0.385</td>
</tr>
</table> (:htmlend:)
- Pipeline slurry
- Slurry Pipeline
L = m.Const(15*5280,'L') # Length of pipeline (ft) W = m.Const(12.67,'W') # Massflow of limestone (lbm/sec) a = m.Const(0.01,'a') # Average lump-size before grinding (ft) pi = m.Const(3.1415927,'pi') # pi
rho_w = m.Const(62.428,'rho_w') # Density of water (lbm/ft^3) mu = m.Const(7.392e-4,'mu') # Viscosity of water (lbm/ft/sec) g = m.Const(32.174,'g') # Gravitational constant (ft/sec^2)
L = 15*5280 # Length of pipeline (ft) W = 12.67 # Massflow of limestone (lbm/sec) a = 0.01 # Average lump-size before grinding (ft) pi = 3.1415927
rho_w = 62.428 # Density of water (lbm/ft^3) mu = 7.392e-4 # Viscosity of water (lbm/ft/sec) g = 32.174 # Gravitational constant (ft/sec^2)
gc = m.Const(32.174049,'gc')
gc = 32.174049
gamma_L = m.Const(168.5,'gamma_L')
gamma_L = 168.5
V = m.Var(value=10 , lb=1 , ub=20 , name='V')
- Volumetric concentration of slurry (Vol limestone/Vol Total)
c = m.Var(value=0.2 , lb=0.01 , ub=0.4 , name='c')
V = m.Var(value=10, lb=1, ub=20, name='V')
- Volumetric concentration of slurry
- (Vol limestone/Vol Total)
c = m.Var(value=0.2, lb=0.01, ub=0.4, name='c')
Dpipe = m.Var(value=0.4 , lb=0.01 , ub=0.5 , name='Dpipe')
Dpipe = m.Var(value=0.4, lb=0.01, ub=0.5, name='Dpipe')
d = m.Var(value=0.008 , lb=0.0008 , name='d') Pt = m.Var(value=1 , name='Pt')
d = m.Var(value=0.008, lb=0.0008, name='d') Pt = m.Var(value=1, name='Pt')
fw = m.Intermediate(-1.5919e-4*y**3+5.5535e-3*y**2-6.8029e-2*y+0.31078,'fw')
fw = m.Intermediate(-1.5919e-4*y**3+5.5535e-3*y**2 -6.8029e-2*y+0.31078)
CdRp2 = m.Intermediate(4*g*rho_w*d**3*(gamma_L-rho_w)/(3*mu**2),'CdRp2') x = m.Intermediate(m.log(CdRp2),'x') Cd = m.Intermediate(m.exp(0.03420*x**2-0.98327*x+6.17176),'Cd')
CdRp2 = m.Intermediate(4*g*rho_w*d**3* (gamma_L-rho_w)/(3*mu**2)) x = m.Intermediate(m.log(CdRp2)) Cd = m.Intermediate(m.exp(0.03420*x**2-0.98327*x+6.17176))
rho = m.Intermediate((1-c)*rho_w+c*gamma_L,'rho')
rho = m.Intermediate((1-c)*rho_w+c*gamma_L)
S = m.Intermediate(gamma_L/rho_w,'S')
S = m.Intermediate(gamma_L/rho_w)
r = m.Intermediate(rho_w/rho,'r') t = m.Intermediate(g*Dpipe*(S-1)/(V**2*m.sqrt(Cd)),'t') f = m.Intermediate(fw*(r+150*c*r*t**1.5),'f')
r = m.Intermediate(rho_w/rho) t = m.Intermediate(g*Dpipe*(S-1)/(V**2*m.sqrt(Cd))) f = m.Intermediate(fw*(r+150*c*r*t**1.5))
dp = m.Intermediate(f*rho*L*V**2/(2*Dpipe*gc),'dp')
dp = m.Intermediate(f*rho*L*V**2/(2*Dpipe*gc))
Area = m.Intermediate(pi*Dpipe**2/4,'Area')
Area = m.Intermediate(pi*Dpipe**2/4)
Q = m.Intermediate(Area*V,'Q')
Q = m.Intermediate(Area*V)
mdot = m.Intermediate(rho*Area*V,'mdot')
mdot = m.Intermediate(rho*Area*V)
Q_L = m.Intermediate(Q*c,'Q_L') # ft^3/sec mdot_L = m.Intermediate(gamma_L*Q_L,'mdot_L') # lbm/sec = (lbm/ft^3) * (ft^3/sec)
Q_L = m.Intermediate(Q*c) # ft^3/sec
- lbm/sec = (lbm/ft^3) * (ft^3/sec)
mdot_L = m.Intermediate(gamma_L*Q_L)
Pf = m.Intermediate(dp*Q,'Pf')
Pf = m.Intermediate(dp*Q)
Pg = m.Intermediate(218*W*(1/m.sqrt(d)-1/m.sqrt(a)),'Pg')
Pg = m.Intermediate(218*W*(1/m.sqrt(d)-1/m.sqrt(a)))
Vc = m.Intermediate((40*g*c*(S-1)*Dpipe/m.sqrt(Cd))**0.5,'Vc')
Vc = m.Intermediate((40*g*c*(S-1)*Dpipe/m.sqrt(Cd))**0.5)
- Velocity must be greater than the critical velocity constraint
- Velocity must be greater than
- the critical velocity constraint
(:description Engineering design and optimization of a heat pump system for pasteurization of milk. Optimization principles are used to design the system.:)
(:description Engineering design and optimization of limestone slurry pipeline. Optimization principles are used to design the system.:)

(:title Limestone Slurry Pipeline Optimization Problem:)
(:title Limestone Slurry Pipeline Optimization:)
A slurry pipeline is a type of pipeline used to transport a mixture of materials suspended in a liquid or gas. These materials are usually particles of solid matter, such as sand, clay, and other minerals, suspended in a liquid base, such as water or oil. Slurry pipelines are used in many industries, including mining, oil and gas, and agriculture.
The optimization of a slurry pipeline depends on the type of slurry and the application. In general, the goal is to minimize the total cost of the pipeline, which includes capital and operating costs. Optimization may involve adjusting the diameter of the pipeline, the type and number of pumps, the use of valves and other controlling devices, and the installation of strainers and other equipment to filter out solids. Other considerations include the environmental impact of the pipeline, safety, and the ability to handle the slurry without damage to the equipment. In some cases, the optimization process may also include the use of additives to improve the flow characteristics of the slurry.
gc = m.Const(32.174049,'gc') # Converstion between lbm and lbf (lbm ft / lbf / s^2) gamma_L = m.Const(168.5,'gamma_L') # Density of limestone (lbm/ft^3)
- Conversion between lbm and lbf (lbm ft / lbf / s^2)
gc = m.Const(32.174049,'gc')
- Density of limestone (lbm/ft^3)
gamma_L = m.Const(168.5,'gamma_L')
V = m.Var(value=10 , lb=1 , ub=20 , name='V') # Average flow velocity (ft/sec) c = m.Var(value=0.2 , lb=0.01 , ub=0.4 , name='c') # Volumetric concentration of slurry (Vol limestone/Vol Total) Dpipe = m.Var(value=0.4 , lb=0.01 , ub=0.5 , name='Dpipe') # Internal pipe diameter (ft) d = m.Var(value=0.008 , lb=0.0008 , name='d') # Average particle size after grinding (ft)
- Average flow velocity (ft/sec)
V = m.Var(value=10 , lb=1 , ub=20 , name='V')
- Volumetric concentration of slurry (Vol limestone/Vol Total)
c = m.Var(value=0.2 , lb=0.01 , ub=0.4 , name='c')
- Internal pipe diameter (ft)
Dpipe = m.Var(value=0.4 , lb=0.01 , ub=0.5 , name='Dpipe')
- Average particle size after grinding (ft)
d = m.Var(value=0.008 , lb=0.0008 , name='d')
(:sourceend:)
(:sourceend:)
Solution Help

See GEKKO documentation and additional example problems.
(:source lang=python:) from gekko import GEKKO m = GEKKO()
- Pipeline slurry
- Constants
L = m.Const(15*5280,'L') # Length of pipeline (ft) W = m.Const(12.67,'W') # Massflow of limestone (lbm/sec) a = m.Const(0.01,'a') # Average lump-size before grinding (ft) pi = m.Const(3.1415927,'pi') # pi
rho_w = m.Const(62.428,'rho_w') # Density of water (lbm/ft^3) mu = m.Const(7.392e-4,'mu') # Viscosity of water (lbm/ft/sec) g = m.Const(32.174,'g') # Gravitational constant (ft/sec^2) gc = m.Const(32.174049,'gc') # Converstion between lbm and lbf (lbm ft / lbf / s^2) gamma_L = m.Const(168.5,'gamma_L') # Density of limestone (lbm/ft^3)
- Variables
V = m.Var(value=10 , lb=1 , ub=20 , name='V') # Average flow velocity (ft/sec) c = m.Var(value=0.2 , lb=0.01 , ub=0.4 , name='c') # Volumetric concentration of slurry (Vol limestone/Vol Total) Dpipe = m.Var(value=0.4 , lb=0.01 , ub=0.5 , name='Dpipe') # Internal pipe diameter (ft) d = m.Var(value=0.008 , lb=0.0008 , name='d') # Average particle size after grinding (ft) Pt = m.Var(value=1 , name='Pt')
- Intermediates
- Reynolds number
Rw = m.Intermediate(rho_w*V*Dpipe/mu,'Rw')
- Friction factor for water (fit empirical correlation)
y = m.Intermediate(m.log(Rw),'y') fw = m.Intermediate(-1.5919e-4*y**3+5.5535e-3*y**2-6.8029e-2*y+0.31078,'fw')
- Dimensionless numbers to obtain drag coefficient
CdRp2 = m.Intermediate(4*g*rho_w*d**3*(gamma_L-rho_w)/(3*mu**2),'CdRp2') x = m.Intermediate(m.log(CdRp2),'x') Cd = m.Intermediate(m.exp(0.03420*x**2-0.98327*x+6.17176),'Cd')
- Slurry density
rho = m.Intermediate((1-c)*rho_w+c*gamma_L,'rho')
- Limestone specific gravity
S = m.Intermediate(gamma_L/rho_w,'S')
- Slurry friction factor
r = m.Intermediate(rho_w/rho,'r') t = m.Intermediate(g*Dpipe*(S-1)/(V**2*m.sqrt(Cd)),'t') f = m.Intermediate(fw*(r+150*c*r*t**1.5),'f')
- Pressure drop (lbf / ft^2)
dp = m.Intermediate(f*rho*L*V**2/(2*Dpipe*gc),'dp')
- Pipe cross-sectional area (ft^2)
Area = m.Intermediate(pi*Dpipe**2/4,'Area')
- Slurry flow rate (ft^3/sec)
Q = m.Intermediate(Area*V,'Q')
- Slurry mass flow rate (lbm/sec)
mdot = m.Intermediate(rho*Area*V,'mdot')
- Limestone mass flow rate (lbm/sec)
Q_L = m.Intermediate(Q*c,'Q_L') # ft^3/sec mdot_L = m.Intermediate(gamma_L*Q_L,'mdot_L') # lbm/sec = (lbm/ft^3) * (ft^3/sec)
- Friction power loss (ft * lbf / sec)
Pf = m.Intermediate(dp*Q,'Pf')
- Grinding power (ft*lbf/sec)
Pg = m.Intermediate(218*W*(1/m.sqrt(d)-1/m.sqrt(a)),'Pg')
- Critical velocity
Vc = m.Intermediate((40*g*c*(S-1)*Dpipe/m.sqrt(Cd))**0.5,'Vc')
- Equations
- Total power (grinding + pumping)
m.Equation(Pt==Pg+Pf)
- Mass flow of limestone
m.Equation(mdot_L==W)
- Velocity must be greater than the critical velocity constraint
m.Equation(V>Vc)
m.Minimize(Pt)
m.solve() print('Optimal Power: ' + str(Pt[0])) (:sourceend:)
(:html:)
<div id="disqus_thread"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
/* * * CONFIGURATION VARIABLES: EDIT BEFORE PASTING INTO YOUR WEBPAGE * * */
var disqus_shortname = 'apmonitor'; // required: replace example with your forum shortname
/* * * DON'T EDIT BELOW THIS LINE * * */
(function() {
var dsq = document.createElement('script'); dsq.type = 'text/javascript'; dsq.async = true;
dsq.src = 'https://' + disqus_shortname + '.disqus.com/embed.js';
(document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0] || document.getElementsByTagName('body')[0]).appendChild(dsq);
})();
</script>
<noscript>Please enable JavaScript to view the <a href="https://disqus.com/?ref_noscript">comments powered by Disqus.</a></noscript>
<a href="https://disqus.com" class="dsq-brlink">comments powered by <span class="logo-disqus">Disqus</span></a>
(:htmlend:)
(:html:) <iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/3bWc9RmxCPQ?rel=0" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe> (:htmlend:)
 This assignment can be completed in groups of two. Additional guidelines on individual, collaborative, and group assignments are provided under the Expectations link.
This assignment can be completed in groups of two. Additional guidelines on individual, collaborative, and group assignments are provided under the Expectations link. This assignment can be completed in groups of two. Additional guidelines on individual, collaborative, and group assignments are provided under the Expectations link.
This assignment can be completed in groups of two. Additional guidelines on individual, collaborative, and group assignments are provided under the Expectations link.(:html:)
<div id="disqus_thread"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
/* * * CONFIGURATION VARIABLES: EDIT BEFORE PASTING INTO YOUR WEBPAGE * * */
var disqus_shortname = 'apmonitor'; // required: replace example with your forum shortname
/* * * DON'T EDIT BELOW THIS LINE * * */
(function() {
var dsq = document.createElement('script'); dsq.type = 'text/javascript'; dsq.async = true;
dsq.src = 'https://' + disqus_shortname + '.disqus.com/embed.js';
(document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0] || document.getElementsByTagName('body')[0]).appendChild(dsq);
})();
</script>
<noscript>Please enable JavaScript to view the <a href="https://disqus.com/?ref_noscript">comments powered by Disqus.</a></noscript>
<a href="https://disqus.com" class="dsq-brlink">comments powered by <span class="logo-disqus">Disqus</span></a>
(:htmlend:)
(:title Limestone Slurry Pipeline Optimization Problem:) (:keywords mining, slurry, pipeline, nonlinear, optimization, engineering optimization, two-bar optimization, engineering design, interior point, active set, differential, algebraic, modeling language, university course:) (:description Engineering design and optimization of a heat pump system for pasteurization of milk. Optimization principles are used to design the system.:)
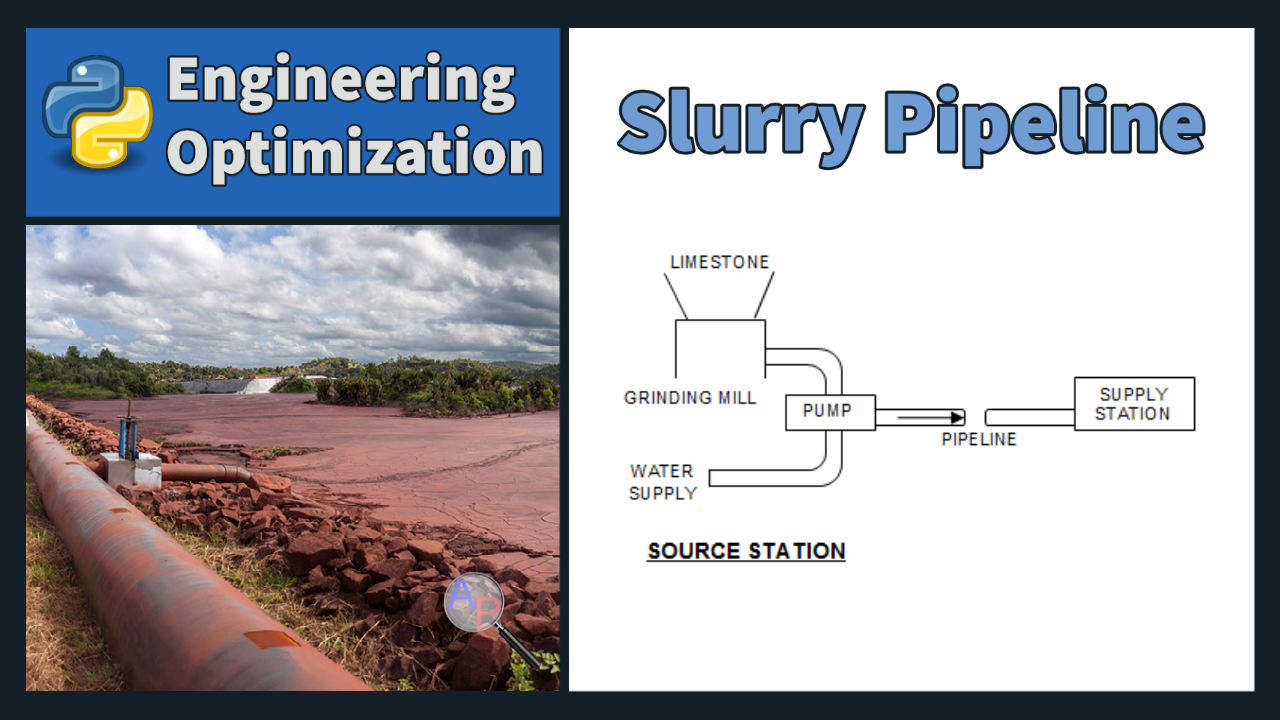
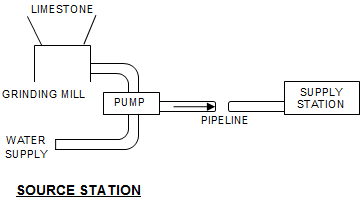
Design a pipeline for transporting crushed limestone from a quarry to a terminal located some distance away, using water as a transporting medium.
Full Slurry Pipeline Assignment

The limestone is crushed at the quarry, mixed with water to form a slurry, and pumped through the pipe. We would like to minimize the operating cost, which is primarily determined by the grinding power and the pumping power.
This problem is taken from James Siddall, Optimal Engineering Design, Dekker.
 This assignment can be completed in groups of two. Additional guidelines on individual, collaborative, and group assignments are provided under the Expectations link.
This assignment can be completed in groups of two. Additional guidelines on individual, collaborative, and group assignments are provided under the Expectations link.