A crane hook is used for lifting and moving heavy objects and is often found in industrial applications. Design a crane hook to carry a load F. The hook has a rectangular cross section with width b (minimum 0.2 mm) and height h.
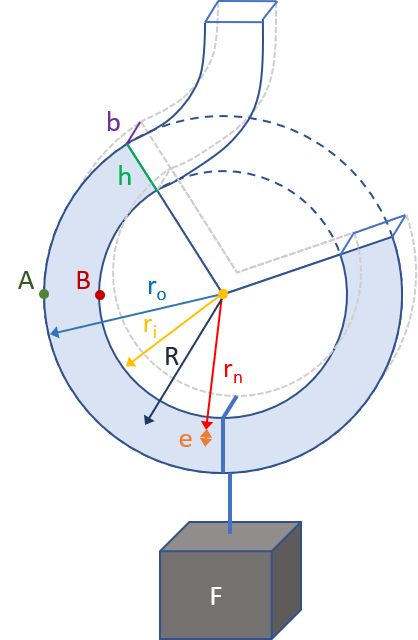
Optimize the crane hook design to minimize the volume of the hook. The hook is manufactured from a complete rectangular wire ring that is clipped and bent to give the final hook shape. The outer radius of the hook is ro and the inner radius is ri with a minimum inner diameter of 3.0 mm. The height is the difference between the outer and inner radius h=ro-ri. The bending moment is M=FR with a force F of 100 N (10.2 kg for a static load on earth). The centroid radius is R and the neutral axis radius is rn.
$$r_n = \frac{h}{\ln\left(r_o/r_i\right)}$$
The difference between the centroid radius and the neutral axis radius is e. The stress at point A is
$$\sigma_A = \frac{M \left(r_o-r_n\right)}{b\;h\;e\;r_o}$$
The stress at point B is
$$\sigma_B = \frac{M \left(r_n-r_i\right)}{b\;h\;e\;r_i}$$
The stress at points A and B should not exceed the yield strength of the steel at 430 N/mm2.
Solution
from gekko import GEKKO
from numpy import pi
m = GEKKO(remote=False)
# Constants
F = 100 # load (N)
S_y = 430 # yield strength of steel (N/mm^2)
# Grade D fine-carbon steel (ASTM A255)
# Variables
r_o = m.Var() # outer radius (mm)
r_i = m.Var(lb=1.5) # inner radius (mm)
b = m.Var(lb=0.2) # hook width (mm)
V = m.Var() # hook volume (mm^3)
# Intermediates
h = r_o - r_i # hook height (mm)
R = (r_o + r_i)/2 # radius of the centroid (mm)
r_n = h/m.log(r_o/r_i) # radius of the neutral axis (mm)
e = R - r_n # R - r_n (mm)
M = F * R # bending moment due to the load
c_o = r_o - r_n # distance from outer to neutral(mm)
c_i = r_n - r_i # distance from inner to neutral(mm)
Area = b*h # cross-sectional area (mm^2)
o_A = (M*c_o/(Area*e*r_o)) # outer stress
o_B = (M*c_i/(Area*e*r_i)) # inner stress
# Equations
m.Equations([
V == pi*(r_o**2-r_i**2)*b, # volume calculation
o_A < S_y, # yield stress @ A < yield strength
o_B < S_y, # yield stress @ B < yield strength
r_i < r_o # constraint for feasibility
])
# Objective
m.Minimize(V)
# Solve
m.options.SOLVER = 3
m.solve()
print('Optimal Volume: ' + str(V[0]))
print('Optimal outer radius: ' + str(r_o[0]))
print('Optimal inner radius: ' + str(r_i[0]))
print('Optimal hook width: ' + str(b[0]))
The optimal solution is:
Optimal Volume: 37.50 mm^2 Optimal outer radius: 3.39 mm Optimal inner radius: 1.50 mm Optimal hook width: 1.29 mm
